Major electric power transmission corridors of the Western United States
Alternating current
One Nevada Path 3, Path 4, Path 5, Path 6, Path 8, Path 9, Path 10-11, Path 14, Path 15, Path 2,1 Path 22, Path 26, Path 45, Path 46, Path 49, Path 51, Path 54, Path 61, Path 62, Path 63, Path 64, Path 66, Path 71, Path 73, Path 75
Direct current
Path 27 (Intermountain) Pacific DC Intertie (Path 65)
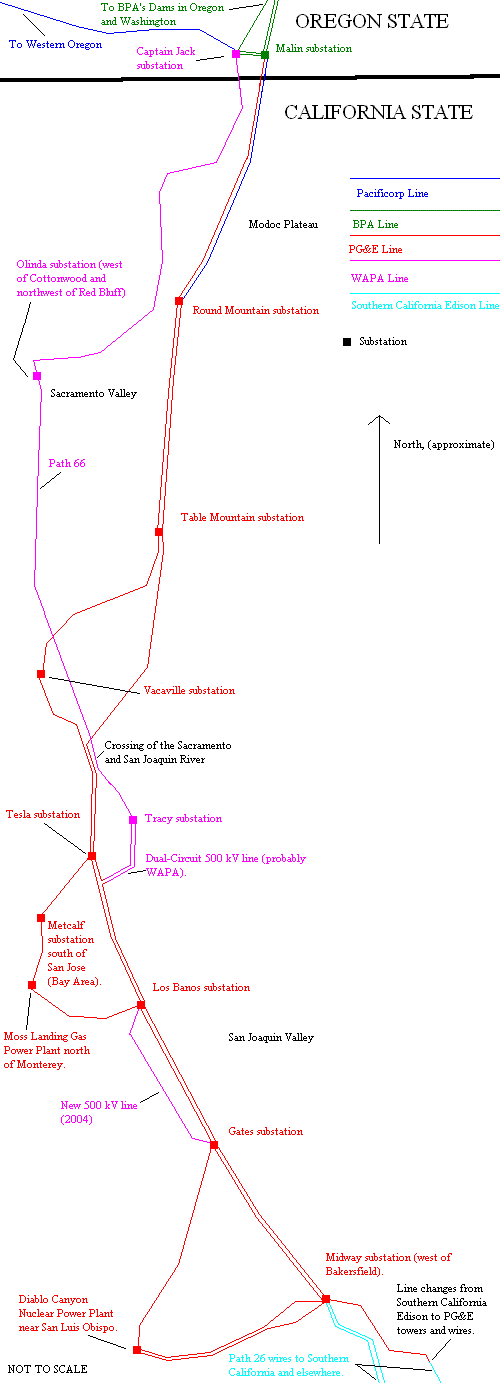
Path 66 can transmit 4,800 MW of electrical power from north to south. From south to north, the system can transmit only 3,675 MW of power.(4)
This TANC 500 kV power line, unlike its PG&E counterparts, is triple-bundled, meaning that it has three-wires per phase, whereas the PG&E lines are only double-bundled, or two wires per phase. In addition, the tower's design is strikingly different from the lighter and wider PG&E tower, and the design also changes significantly as one goes from north to south on WAPA's 346 mi (557 km) 500 kV line.(3)